Vaccination plays a crucial role in safeguarding public health by preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Vaccines have been instrumental in controlling and eradicating diseases that were once widespread and caused significant morbidity and mortality. They have saved countless lives and continue to be one of the most effective preventive measures available.
By stimulating the immune system to produce an immune response without causing the actual disease, vaccines prepare the body to recognize and fight specific pathogens. This is important because it helps to develop immunity and protect individuals from future infections.
Vaccination offers several benefits, such as:
Preventing the spread of diseases within communities
Protecting individuals from severe illness and complications
Reducing the burden on healthcare systems
Contributing to herd immunity, which protects vulnerable populations
Helping to control and eliminate diseases globally
Vaccine Schedule
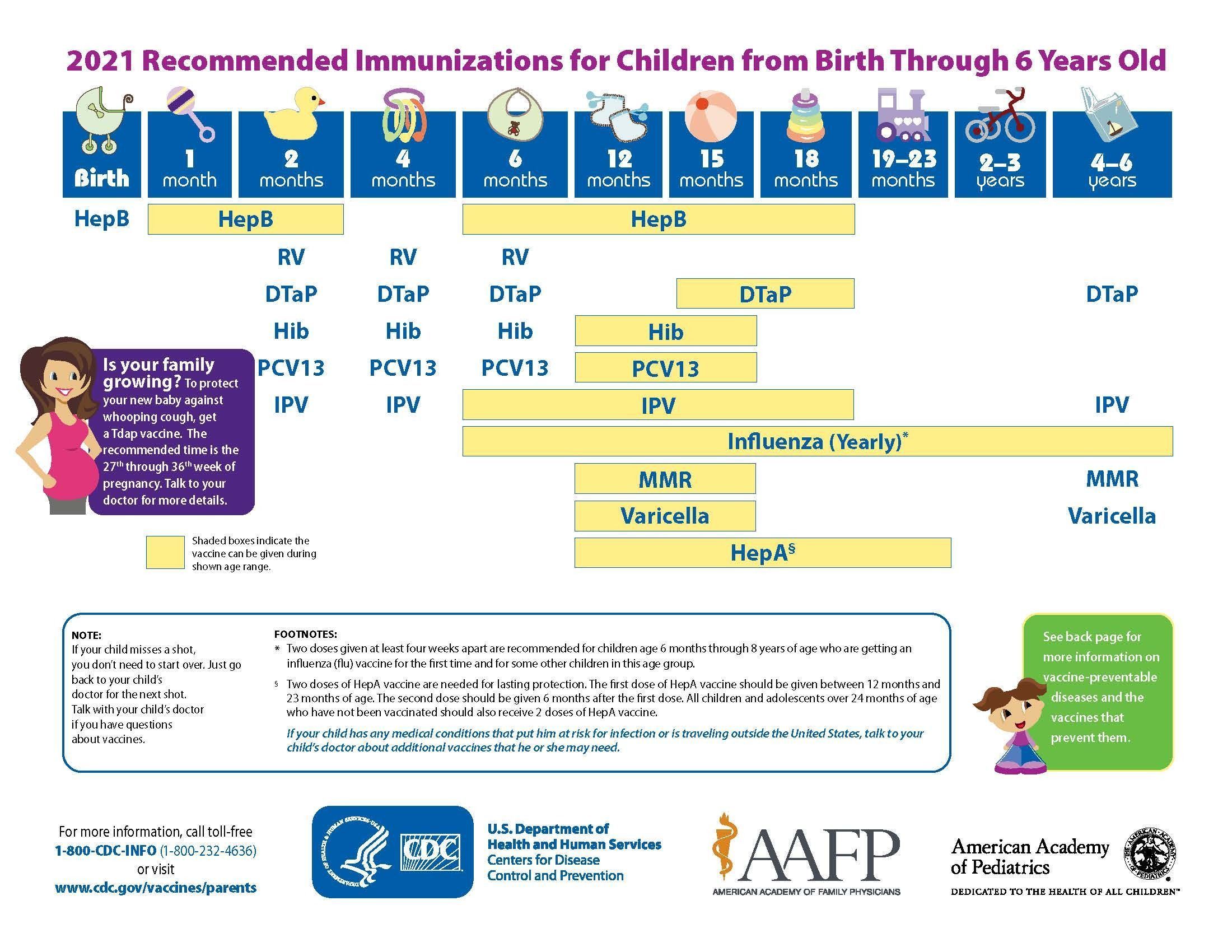
The vaccination schedule outlines the recommended timing and sequence of vaccines for different age groups. It is designed to ensure that individuals receive the right vaccines at the right time to provide optimal protection. Following the suggested schedule is essential for achieving the desired immune response and preventing vaccine-preventable diseases.
The vaccine schedule may vary slightly depending on factors such as the country, individual health conditions, and specific vaccine guidelines. It is important to consult healthcare providers or refer to official sources for accurate and up-to-date information.
Here is a general overview of the vaccine schedule for children:
Age
Vaccines
Birth
Hepatitis B
2 months
Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (DTaP); Rotavirus; Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib); Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV); Inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV)
4 months
DTaP; Rotavirus; Hib; PCV; IPV
6 months
DTaP; Rotavirus; Hib; PCV; IPV; Influenza (seasonal)
12-15 months
MMR (Measles, mumps, rubella); Varicella (Chickenpox); Hib; PCV; Hepatitis A
4-6 years
DTaP; MMR; Varicella; IPV
The vaccine schedule continues beyond childhood to provide additional booster doses and vaccines for specific diseases throughout life. Some vaccines may also be recommended for individuals with certain medical conditions or specific risks.
Ensuring Vaccine Safety
Vaccine safety is a critical aspect of vaccination programs. Extensive research, testing, and monitoring are conducted to ensure the safety and effectiveness of vaccines before they are approved for public use.
Additionally, regulatory bodies and health organizations continuously monitor vaccines for any potential adverse effects. These systems play a crucial role in identifying and addressing any rare side effects or safety concerns related to vaccines.
It is important to trust credible sources for information about vaccine safety and consult healthcare professionals for any concerns or questions. They can provide accurate information and address any doubts or misconceptions.
In Conclusion
Vaccination is of utmost importance to protect individuals and communities from serious and preventable diseases. By adhering to the recommended vaccine schedule and ensuring vaccine safety, we can collectively contribute to controlling and eliminating various infectious diseases.
Through continued vaccination efforts, we can strive to create a healthier, safer, and more resilient society for all.